Table of contents
- Hey Everyone 👋👋
- ✅Basics of Bit Manipulation
- 🔰 Tips and Tricks
- 🌟Divide and Multiply by 2
- 🌟Check if a given number is even
- 🌟Check if a given number is a power of 2
- 🌟Swap two numbers without a temporary variable
- 🌟Get ith bit
- 🌟Set ith bit
- 🌟Unset ith bit
- 🌟Toggle ith bit
- 🌟Count number of set bits
- 🌟Most significant set bit and least significant set bit
- 🌟Highest power of 2 less than or equal to the given number
- 🌟 Count number of set bits on ith position from a list of numbers
- 🎯Final thoughts
Hey Everyone 👋👋
As a programmer we often work with multiple data types such as int, float etc, (Pythonista's be like: 😎😂" ) but sometimes we need to deal with bits and bytes as computers do not understand words and numbers the way we do.
Bits and bytes can be scary at some times while solving a problem or doing competitive programming. If the basics of the same are not clear they can be a nightmare. Dealing with such questions need some basics and some tips which we will discuss in this article.
Without further explanation, let us begin.

✅Basics of Bit Manipulation
Every number can be represented in a binary form, this binary form has consists of 1 and 0s which we call as and bits. Manipulating these bits to get the desired output is known as bit manipulation.
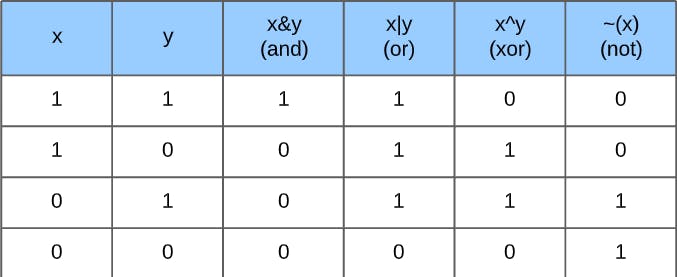
There are 6-bit operators which we should know, these are operators are really important and help crack most of the questions. Always remember to think in bits when you approach a problem related to bit manipulation.

AND-&- If both inputs are true, then the output is true.OR-|- If either of the inputs is true, then the output is true.XOR-^- EXCLUSIVE OR - If either, but not both, of the inputs, is true, then the output is true.NOT-~- Negation operator takes each bit in a number and toggles itLeft Shift-<<- The most-significant bit is lost, and a 0 bit is inserted on the other end.
Eg :
0110 << 1 = 1100
0110 << 3 = 11000
Right Shift->>- The least-significant bit is lost and a 0 is inserted on the other end.
Eg :
1111 >> 1 = 0111
1111 >> 3 = 0001
Here is a truth table to understand the rest of the operators :
🔰 Tips and Tricks

🌟Divide and Multiply by 2
To divide by 2 we right shift the number by 1 and to multiply by 2 we left shift the number 1.
int divideby2(int n){
return n >> 1;
}
int multiplyby2(int n){
return n << 1;
}
🌟Check if a given number is even
If a number is even then and of that number with 1 will yield 0.
bool isEven(int n){
return (n & 1) == 0;
}
🌟Check if a given number is a power of 2
To do this we use and operator, if a number n is the power of 2 then doing and operation of n with n-1 will give 0.
bool isPowerof2(int n){
if(n==0)
return false;
return (n & (n - 1)) == 0;
}
🌟Swap two numbers without a temporary variable
We can swap two numbers with xor operation.
void swap(int& a, int& b){
a = a ^ b;
b = b ^ a;
a = a ^ b;
cout<<a<<" "<<b<<endl;
}
🌟Get ith bit
To get the ith we right shift by i bits.
Note: The indexing of i in this article starts from 0.
int getbit(int n, int i){
return (n >> i);
}
🌟Set ith bit
To set the ith bit you can use a bitmask with the ith bit set, meaning you create another binary number with ith bit set and do or operation,
int setbit(int n, int i){
return n | (1 << i);
}
🌟Unset ith bit
To unset ith bit create a bitmask with ith unset bit and rest all set bits, we can do this by negation operator and left shift operator and do and operation which will unset the ith bit.
int unsetbit(int n, int i){
return n & ~(1 << i);
}
🌟Toggle ith bit
To toggle ith bit we create a bitmask with the ith bit set and do the xor operation.
int togglebit(int n, int i){
return n ^ (1 << i);
}
🌟Count number of set bits
To count set bits we do and operation with 1 to check if the last bit is set and left shift n until it becomes zero.
int countsetbits(int n){
int count = 0;
while(n){
count+=n&1;
n=n>>1;
}
return count;
}
🌟Most significant set bit and least significant set bit
For LSB we right shift and do and operation with 1.
If it is set we return the position.
int lowestsetbit(int n){
int i = 0;
while(n){
if(n & 1)
return i;
n = n >> 1;
i++;
}
return -1;
}
For MSB we right shift until n is not zero.
int highestsetbit(int n){
int i = 0;
while(n){
n = n >> 1;
i++;
}
return i;
}
🌟Highest power of 2 less than or equal to the given number
We first get the most significant bit position and left-shift 1 by i.
int highestPowerof2(int n){
int i = 0;
while(n){
n = n >> 1;
i++;
}
return (1 << i);
}
🌟 Count number of set bits on ith position from a list of numbers
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> getsetbits(vector<int> arr){
vector<int> count(32,0);
for(int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 32; j++)
count[j] += (1&(arr[i] >> j));
return count;
}
int main(){
vector<int> arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
vector<int> count = getsetbits(arr);
for(int i = 0; i < count.size(); i++)
cout<<count[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}
You can explore more here.
🎯Final thoughts
Bit manipulation is necessary for competitive programming. It helps you think in bits and bytes. With these tips and tricks, you will be able to solve many problems. To get a hang of Bit manipulation try to solve as many questions as you can, each question will teach you different applications of these tips and tricks.
Here are some practice problems :
Amazing !🎉 Congrats on making it to the end of the article, I hope you got to learn a lot. Feel free to use these tips and tricks in your programming solutions. Give me a follow if you would love to see such kinds of articles.
Adios Amigos !😎😎


